Daily
Current Affairs Analysis
16
September 2024
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
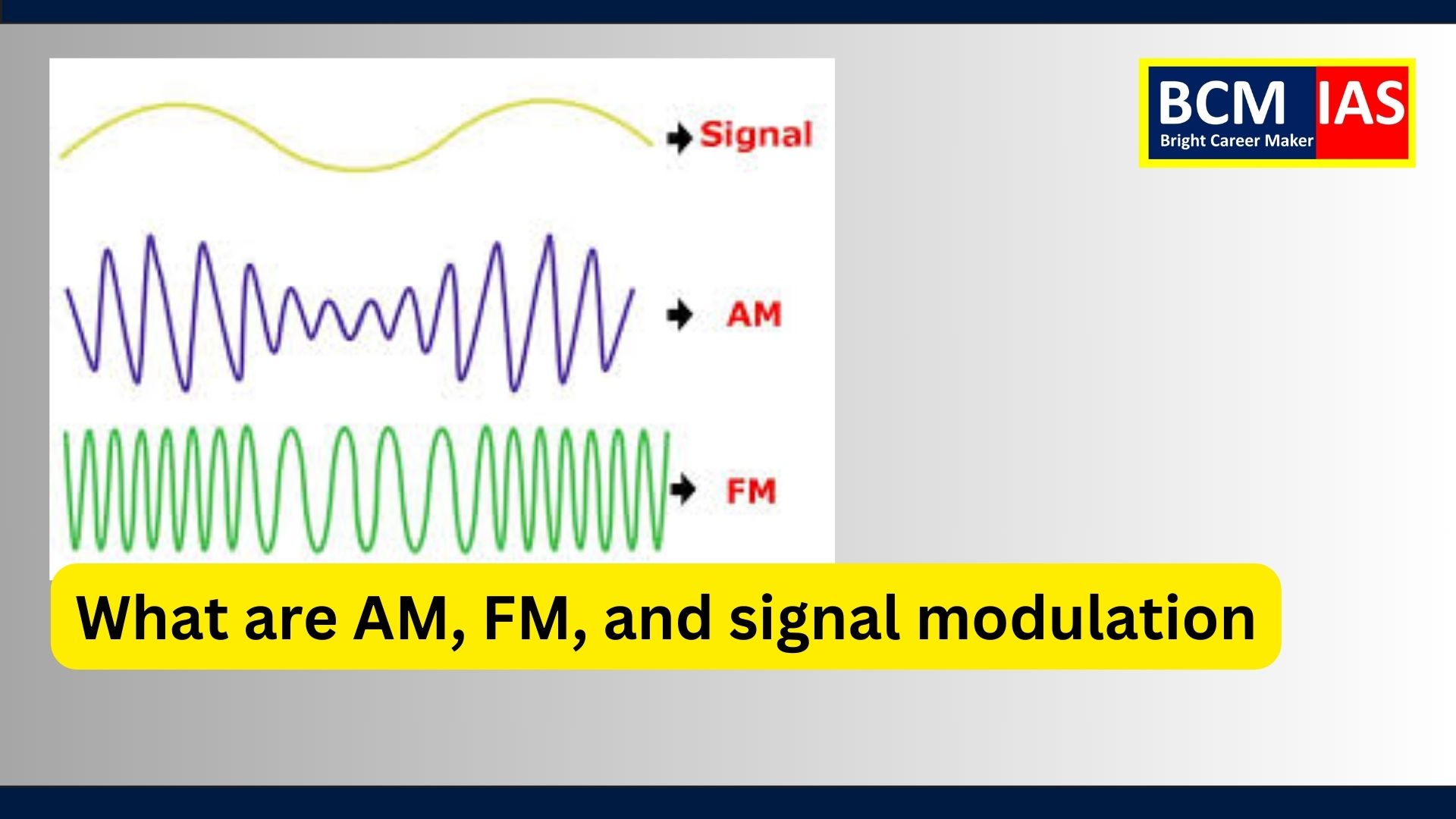
What are AM, FM, and signal modulation?
Meaning of Headline-
The article titled "What are AM,
FM, and signal modulation?" explains different types of signal
modulation techniques used in broadcasting, particularly Amplitude
Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM). The concept is
fundamental to understanding how radio signals are transmitted and received by
adjusting various wave properties such as amplitude, frequency, and phase. It
also introduces Phase Modulation (PM), which is another type of modulation technique.
Prelims
Syllabus (General Studies Paper I):
This article can be linked to the Science
and Technology portion of the syllabus, particularly under the following
topics:
- Current
developments in science and technology and their applications in everyday
life: Radio
communication, signal modulation techniques, electromagnetic waves, and
their uses in real-world broadcasting are all relevant.
- Physics
fundamentals:
Concepts like electromagnetic waves, wave properties (amplitude,
frequency), and how they are used for transmitting information (radio
waves).
Mains
Syllabus (General Studies Paper III):
- Science
and Technology – developments and their applications and effects in
everyday life: This
topic covers how AM, FM, and PM are used in broadcasting and communication
technologies.
- Indigenization
of technology and developing new technology: Understanding
the evolution of broadcasting methods, including the shift from analog to
digital transmission and its impact on the communication sector.
- Information
and Communication Technology (ICT): The article touches upon analog vs. digital communication
systems, which are vital in ICT development and broadcasting technologies.
Interview
(Personality Test):
In the interview, you might be asked about
real-life applications of science and technology in governance and daily life.
Questions might include:
- How do
AM and FM technologies impact radio communication?
- What
are the advantages and limitations of different modulation techniques in
the context of technological advancements in India?
News Explanation
I. Introduction
The article discusses signal modulation
techniques, primarily Amplitude Modulation (AM), Frequency Modulation
(FM), and Phase Modulation (PM). These methods are crucial for
transmitting information like radio waves, adjusting wave properties to improve
clarity, minimize interference, and ensure efficient communication over
distances.
This concept is part of the Science and
Technology domain in the UPSC syllabus and is relevant for understanding
developments in telecommunications, broadcasting, and ICT infrastructure in
India.
II. Explanation of Key
Concepts in the Article
1.
Signal
Modulation:
o
A process by which properties of a wave (such as
amplitude, frequency, or phase) are adjusted to transmit information.
o
These waves are primarily electromagnetic and
travel through various mediums (air, fiber optics, etc.).
o
Signal modulation helps achieve clear transmission,
reducing interference and enhancing the quality of communication, particularly
in radio, TV, and wireless technologies.
2.
Types of
Modulation:
o Amplitude Modulation (AM):
§
Modifies the amplitude (height) of the wave to carry
information.
§
Example: Used in AM radio broadcasting (e.g., "You are listening to
783 AM"), which operates in the lower frequency range but can cover large
distances.
o Frequency Modulation (FM):
§
Alters the frequency of the wave (the number of wave
cycles per second) to transmit sound or information.
§
Example: FM broadcasting (e.g., "Welcome to 100.1 FM Gold"), used for
clearer sound quality with less static interference but over shorter
ranges.
o Phase Modulation (PM):
§
Adjusts the phase of the wave, i.e., the shift in wave
cycles, to convey information.
§
Example: Common in digital communication systems such as Wi-Fi and satellite
communications.
3.
Analog vs.
Digital Modulation:
o
Analog Signals: Continuous waves that vary in amplitude or frequency.
o
Digital Signals: Discrete signals represented by binary code (0s and 1s), which are
clearer and more efficient in modern telecommunications.
Analysis
and Key Takeaways
1.
Key
Insights from the Article:
o
Amplitude
Modulation (AM) is suitable
for long-range broadcasting but is more prone to noise.
o
Frequency
Modulation (FM) offers
higher quality transmission with reduced static but is limited in range.
o
Phase
Modulation (PM) is highly
used in modern digital communication systems such as Wi-Fi and television
signals due to its ability to transmit data efficiently over shorter
distances.
2.
Current
Developments:
o
The move from analog to digital
technologies across broadcasting and communication systems reflects the modernization
of India's ICT sector.
o
Digital
India initiatives are
dependent on clear, interference-free communication, for which modulation
techniques like FM and PM are integral.
3.
Government
Policies:
o
The role of spectrum management in ensuring
equitable access to communication services is a crucial area in public policy
and governance, particularly in sectors like public broadcasting, telecommunication,
and disaster response.
V. Conclusion
For UPSC IAS aspirants, understanding
signal modulation technologies like AM, FM, and PM is critical in developing a
comprehensive view of the Science and Technology syllabus. This
knowledge not only helps in grasping technological advancements but also
their real-world implications in governance, communication, and development. By
tying these concepts to broader initiatives like Digital India, Smart
Cities Mission, and telecom sector reforms, candidates can
articulate the importance of technology in transforming public services and
infrastructure, which is relevant for both Mains and the Interview stages.
Mains Probable Question
Discuss the
significance of signal modulation techniques like AM, FM, and PM in modern
communication systems.
Model Answer
1.
Introduction
Signal
modulation is a pivotal technique in the field of modern communication that
allows the transmission of information across long distances. Techniques like Amplitude
Modulation (AM), Frequency Modulation (FM), and Phase Modulation
(PM) are fundamental methods that adjust various wave properties to
transmit signals effectively. In today’s era of advanced communication,
understanding these modulation techniques is crucial for ensuring that clear,
accurate information can be sent and received, whether through radio,
television, or digital platforms. Modulation enhances communication by
mitigating interference, ensuring signal clarity, and expanding the distance
over which signals can be transmitted.
In this
context, AM, FM, and PM are the backbone of communication technologies such as
radio and television broadcasting, wireless communication, and even some
aspects of digital data transmission. This essay delves into the significance
of signal modulation, explaining the role and mechanics of each method,
along with exploring how they contribute to the evolving landscape of modern
communication.
2.
Demand of the Question
Amplitude
Modulation (AM), Frequency Modulation (FM), and Phase
Modulation (PM) are modulation techniques used to encode information onto a
carrier wave for efficient transmission. Each method has unique properties and
advantages based on how they handle signal interference, noise, and
transmission distances.
- Amplitude Modulation (AM): This
method involves varying the amplitude of the carrier wave in relation to
the information signal. AM was the earliest form of signal modulation and
remains significant for long-distance transmission. Its frequency range
typically spans from 535 kHz to 1,705 kHz. While AM is susceptible to
interference and noise, especially from lightning or other natural
phenomena, it allows long-range communication, making it useful for
broadcasting news and entertainment over large geographical areas. The
energy efficiency of AM is relatively lower, as much of the power is used
in transmitting the carrier rather than the actual information.
- Frequency Modulation (FM): In
contrast to AM, FM varies the frequency of the carrier wave in line with
the information signal. This provides significant advantages in terms of
noise resistance and overall sound quality. FM is particularly valued in
areas of high noise or interference, such as urban environments. With a
frequency range typically between 88 to 108 MHz, FM transmissions produce
clearer sound quality and are less susceptible to amplitude-based
interference, although they have a relatively shorter transmission range
compared to AM. FM’s focus on signal clarity over long distances makes it
the preferred method for high-fidelity music and entertainment
broadcasting.
- Phase Modulation (PM): PM
involves varying the phase of the carrier wave to encode information.
While similar to FM, PM adjusts the carrier's phase rather than its
frequency. This method ensures efficient bandwidth usage and is often
combined with FM in digital communication systems to improve data
transmission. PM is widely used in wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi
and digital television, as it provides a high level of interference
resistance and allows for clear data transmission.
Role
in Modern Communication Systems:
- These modulation techniques provide the
foundation for analog communication systems like AM/FM radio
broadcasts and TV signals. However, with the evolution of technology,
modulation methods like PM and frequency modulation are
integrated into digital communication systems such as Wi-Fi,
Bluetooth, and cellular networks.
- Signal modulation is also critical for ensuring
that multiple signals can travel simultaneously on the same channel
without interference, a technique known as multiplexing. This
capability is essential for ensuring efficient communication in densely
populated urban environments where signal traffic is high.
Importance
of Signal Modulation:
- Modulation enables communication over long
distances, bypassing limitations imposed by line-of-sight transmission.
AM’s ability to travel long distances, despite interference challenges, is
particularly useful in rural or remote regions. FM, with its clear sound
quality, caters to areas requiring precise sound transmission, such as
radio stations in urban settings.
- Technological adaptation:
Modulation techniques have evolved alongside technology. From being
central to analog broadcasts, modulation now plays a critical role in modern
digital systems like Wi-Fi, cellular networks, and even fiber-optic
communication, which rely on phase and frequency changes for data
transmission.
Challenges
in Transition:
- As the world shifts towards digital
communication, traditional modulation techniques are evolving. Analog
modulation systems like AM and FM are being replaced by digital
modulation techniques, such as Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
(QAM) and Phase-Shift Keying (PSK). While this transition
offers improved efficiency and bandwidth utilization, it requires upgrading
infrastructure, a significant challenge for countries with large
analog systems in place.
3.
Way Forward
As technology
continues to advance, signal modulation techniques must adapt to meet the
growing demand for faster, more reliable communication systems. This can
be achieved through the following strategies:
- Digital Transition: Many
analog systems, such as AM and FM broadcasting, are slowly being replaced
by digital communication methods. The shift towards digital modulation,
such as QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) and PSK (Phase
Shift Keying), should be encouraged for their higher data rates
and better spectrum efficiency. However, a careful balance is
needed to ensure that rural areas dependent on analog systems are not left
behind during this transition.
- Research and Development (R&D): Continuous innovation is essential to develop modulation techniques
that can handle larger data volumes and greater distances.
Focused research on improving PM and FM for 5G networks
and the upcoming 6G could provide solutions for the challenges of signal
interference and bandwidth limitations.
- Capacity Building and
Infrastructure Enhancement: To
support advanced modulation systems, countries must invest in upgrading
their communication infrastructure. This involves expanding the
availability of broadband and fiber-optic networks and ensuring
that existing AM and FM broadcasters have access to modern tools that
reduce interference and enhance signal quality.
- Spectrum Allocation: Governments should prioritize effective spectrum management
to allocate frequency bands in ways that minimize interference and
congestion. By efficiently managing the electromagnetic spectrum,
modulation techniques can work at their optimal capacity, ensuring the
best possible communication quality. The role of international
organizations, like the International Telecommunication Union (ITU),
in maintaining global standards should also be acknowledged and further
supported.
- Public Awareness and Accessibility: While
modern modulation methods promise greater efficiency, their success also
hinges on public accessibility. Educational initiatives should be
undertaken to ensure that individuals, particularly in remote areas,
understand how these changes will benefit them. For example, digital radio
services (like DRM – Digital Radio Mondiale) can replace AM
to offer better sound quality and robustness in signal reception.
Conclusion:
Signal modulation techniques like AM, FM, and PM have revolutionized
communication systems over the last century. With the growing complexity of
communication demands, especially in an era dominated by digital
technologies, the ability of these modulation techniques to evolve is
paramount. While traditional analog modulation remains relevant, the future
lies in the integration of digital modulation systems that offer greater
efficiency, reliability, and scalability. Policymakers and communication
specialists must focus on ensuring a smooth transition, prioritizing
infrastructure upgrades, and promoting public awareness for a future-ready
communication system.
MCQs for Prelims Practice
1. Which of
the following statements about Amplitude Modulation (AM) is correct?
a) AM varies the frequency of the carrier wave to transmit information.
b) AM varies the amplitude of the carrier wave to transmit information.
c) AM is immune to interference from natural sources like lightning.
d) AM has a shorter transmission range than Frequency Modulation (FM).
Answer: b) AM varies
the amplitude of the carrier wave to transmit information.
Explanation: Amplitude Modulation (AM) works by varying the amplitude of
the carrier wave to encode information, such as sound or data. It is prone to
interference from natural sources, such as lightning, and is used primarily for
long-distance radio transmission.
2. In Frequency Modulation (FM),
which of the following properties of the carrier wave is varied?
a) Amplitude
b) Frequency
c) Wavelength
d) Phase
Answer: b) Frequency
Explanation: Frequency Modulation (FM) involves varying the frequency of
the carrier wave in accordance with the information being transmitted. This
results in better sound quality and less susceptibility to interference,
although FM has a shorter transmission range than AM.
3. Which of the following modulation
techniques is most commonly used for television and Wi-Fi communication?
a) Amplitude Modulation (AM)
b) Frequency Modulation (FM)
c) Phase Modulation (PM)
d) Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM)
Answer: c) Phase
Modulation (PM)
Explanation: Phase Modulation (PM) is widely used in modern digital
communication technologies, including Wi-Fi and digital television, due to its
efficient use of bandwidth and resistance to interference.
4. What is the main advantage of
Frequency Modulation (FM) over Amplitude Modulation (AM)?
a) FM signals can travel longer distances than AM signals.
b) FM is less susceptible to interference from external sources.
c) FM requires less bandwidth than AM.
d) FM signals are used exclusively for analog communication.
Answer: b) FM is
less susceptible to interference from external sources.
Explanation: Frequency Modulation (FM) provides superior sound quality
and is less prone to noise and interference compared to Amplitude Modulation
(AM), which makes it ideal for broadcasting music and entertainment.
5. Which of the following best
describes the role of signal modulation in communication systems?
a) It increases the amplitude of transmitted signals to improve clarity.
b) It allows multiple signals to travel simultaneously on the same channel
without interference.
c) It limits the transmission range of signals to prevent interference with
other systems.
d) It prevents data loss by encoding information in binary format.
Answer: b) It allows
multiple signals to travel simultaneously on the same channel without
interference.
Explanation: Signal modulation enables multiple signals to be
transmitted on the same frequency band without causing interference, a process
known as multiplexing. This is essential for efficient use of the communication
spectrum, especially in densely populated areas.



Comments on “What are AM, FM, and signal modulation”