Indian Equatorial Electrojet
Model
1. Why in News?
- Scientists from the Indian Institute of
Geomagnetism (IIG), Navi Mumbai, have developed the Indian
Equatorial Electrojet (IEEJ) Model to predict the Equatorial
Electrojet (EEJ) over the Indian sector.
- Significance: The model aids in
understanding equatorial ionospheric processes with practical applications
across various domains.
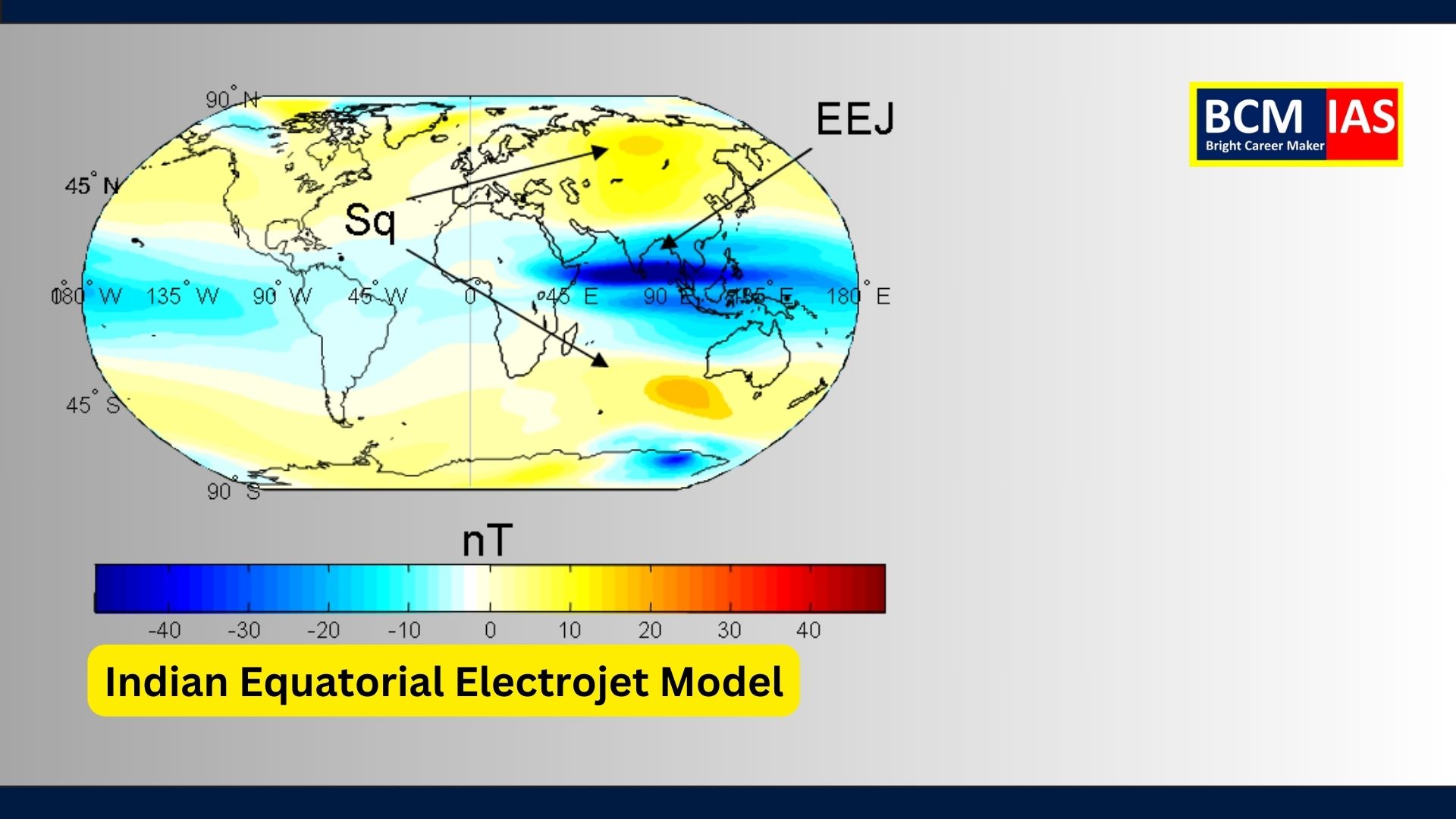
2. What is the Equatorial
Electrojet (EEJ)?
- Definition: A concentrated electric
current flowing eastward in the Earth’s ionosphere, approximately at a
height of 105-110 km near the geomagnetic equator.
- Location: India’s southern tip lies
close to the geomagnetic equator, where this intense current exists.
3. Features of the IEEJ Model
- Web Interface:
- Enables simulations of EEJ for different dates
and varying solar activity conditions.
- Practical Applications:
- Satellite orbital dynamics:
Helps predict the effects of EEJ on satellite trajectories.
- GNSS-based navigation/positioning:
Improves accuracy of GPS systems.
- Satellite communication links:
Mitigates ionospheric disturbances affecting communication.
- Power grids and pipelines:
Monitors geomagnetic storms that can disrupt infrastructure like
transmission lines and oil pipelines.
4. Understanding the Ionosphere
- Nature:
- A region of the Earth’s upper atmosphere, not a
distinct layer, but overlapping with the mesosphere, thermosphere,
and exosphere.
- Contains ions, created when solar radiation
ionizes atmospheric molecules.
- Significance:
- Reflects radio waves, enabling long-distance
communication.
- Grows or shrinks based on solar energy
absorption.
5. Atmospheric Divisions Based on
Thermal and Chemical Composition
1. Thermal
Composition:
o Divided
into layers: Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere,
and Exosphere.
2. Chemical
Composition:
o Homosphere:
§ Extends up
to 90 km; composition of gases like nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon, and
trace gases is uniform.
§ Includes Troposphere,
Stratosphere, and Mesosphere.
o Heterosphere:
§ Beyond 90
km, gases are not evenly mixed due to low turbulence.
§ Includes Thermosphere
and Exosphere.
6. Significance of IEEJ Model
- Scientific Advancement:
Improves understanding of equatorial ionospheric processes crucial for
space and geosciences.
- Economic Impacts:
Reduces risks associated with geomagnetic storms on communication and
power grids.
- Global Applications:
Contributes to global efforts in space weather prediction and management.
7. Related UPSC Previous Year
Questions (PYQs)
- 2013 Question: Dynamic changes on
Earth’s surface are driven by factors like electromagnetic radiation,
geothermal energy, gravitational force, plate movements, Earth’s rotation,
and revolution.
- Answer: (d) All factors contribute.
- 2011 Question: Ionosphere
facilitates radio communication not due to ozone but because it reflects
radio waves via ionized particles.
- Answer: (d) Neither 1 nor 2.
8. Conclusion
The IEEJ Model represents a
significant achievement in space weather research, enhancing India's capacity
to manage the effects of ionospheric disturbances on critical infrastructure
and satellite operations. This aligns with the growing focus on advancing space
and geomagnetic studies for both national and global benefits.
Mains Question & Answer
Question:
Discuss the significance of the Indian Equatorial Electrojet
(IEEJ) Model in understanding equatorial ionospheric processes. How can this
model contribute to critical sectors such as navigation, communication, and
infrastructure management?
Answer:
Introduction
The Indian Equatorial Electrojet
(IEEJ) Model, developed by the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism (IIG), is a
pioneering tool designed to predict the behavior of the Equatorial Electrojet
(EEJ) over the Indian sector. This development marks a significant advancement
in space weather modeling and ionospheric studies, addressing challenges in
satellite communication, navigation, and infrastructure resilience.
Significance of the IEEJ Model
1. Understanding
Equatorial Electrojet:
o The Equatorial
Electrojet (EEJ) is a concentrated electric current flowing in the
ionosphere near the geomagnetic equator.
o The IEEJ
Model uses ground-based magnetometers to simulate EEJ behavior under varying
solar activity and geomagnetic conditions.
2. Scientific
Applications:
o Facilitates
research on equatorial ionospheric processes and their interaction with the
Earth’s magnetic field.
o Enhances
the understanding of geomagnetic equator dynamics.
3. Technological
Contributions:
o GNSS-based
Navigation: Improves GPS accuracy by modeling ionospheric disturbances
affecting satellite signals.
o Satellite
Communication: Predicts disruptions in communication links caused by
ionospheric anomalies.
o Satellite
Orbital Dynamics: Assists in predicting the impact of geomagnetic
forces on satellite trajectories.
4. Infrastructure
Management:
o Electrical
Power Grids: Monitors and mitigates the impact of geomagnetic storms on
power transmission lines.
o Oil and Gas
Pipelines: Identifies potential risks to pipelines from
geomagnetic-induced currents.
Relevance to Critical Sectors
1. Space
Technology:
o Supports
India’s growing space program by improving satellite reliability and
communication resilience.
2. Energy
Sector:
o Reduces
vulnerabilities in power grids during geomagnetic disturbances, ensuring energy
security.
3. Disaster
Management:
o Helps
forecast space weather events, aiding in disaster preparedness for geomagnetic
storms.
Challenges
- Data Availability:
Dependence on accurate and real-time ionospheric data.
- Global Collaboration:
Requires integration with global space weather prediction models for
enhanced effectiveness.
- High Costs: Development and maintenance
of such models are resource-intensive.
Way Forward
- Enhanced Research:
Strengthen funding for space weather research and ionospheric studies.
- International Partnerships:
Collaborate with global agencies like NASA and ESA for improved model
accuracy.
- Capacity Building:
Train scientists and engineers in ionospheric modeling and geomagnetic
research.
Conclusion
The Indian Equatorial Electrojet
(IEEJ) Model is a transformative tool in ionospheric and geomagnetic studies,
contributing to advancements in navigation, communication, and infrastructure
protection. Its development underlines India’s commitment to leveraging space
technology for national and global benefits.
MCQs for Practice
1. Consider the following statements
regarding the Equatorial Electrojet (EEJ):
1. The EEJ is
a concentrated electric current flowing in the Earth’s ionosphere near the
geomagnetic equator.
2. It occurs
at a height of approximately 10-15 km above the Earth’s surface.
3. India’s
southern tip lies close to the geomagnetic equator where the EEJ is prominent.
Which of the statements given above
is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (b) 1 and
3 only
2. Which of the following is NOT a
practical application of the Indian Equatorial Electrojet (IEEJ) Model?
(a) Improving satellite navigation
and positioning systems.
(b) Monitoring earthquakes and predicting tsunamis.
(c) Assisting satellite communication links.
(d) Reducing the impact of geomagnetic storms on power grids.
Answer: (b)
Monitoring earthquakes and predicting tsunamis.
3. The ionosphere, where the
Equatorial Electrojet (EEJ) occurs, is characterized by:
1. Reflection
of radio waves enabling long-distance communication.
2. High concentrations
of electrically charged particles called ions.
3. A stable
and homogenous composition of atmospheric gases.
Select the correct answer using the
codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Answer: (a) 1 and
2 only
4. With reference to the
atmospheric composition, which of the following layers is part of the
Heterosphere?
1. Troposphere
2. Stratosphere
3. Thermosphere
4. Exosphere
Select the correct answer using the
codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2, and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Answer: (b) 3 and
4 only
5. Which of the following factors
influence the position of the geomagnetic equator?
(a) Plate tectonics and seismic
activities.
(b) Variations in the Earth's magnetic field.
(c) Gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun.
(d) Earth’s rotation and revolution.
Answer: (b)
Variations in the Earth's magnetic field.



Comments on “Indian Equatorial Electrojet Model”